Automated Gardening
So it turns out that I am too lazy to water my plants, but not too lazy to spend many hours automating the watering of my plants.
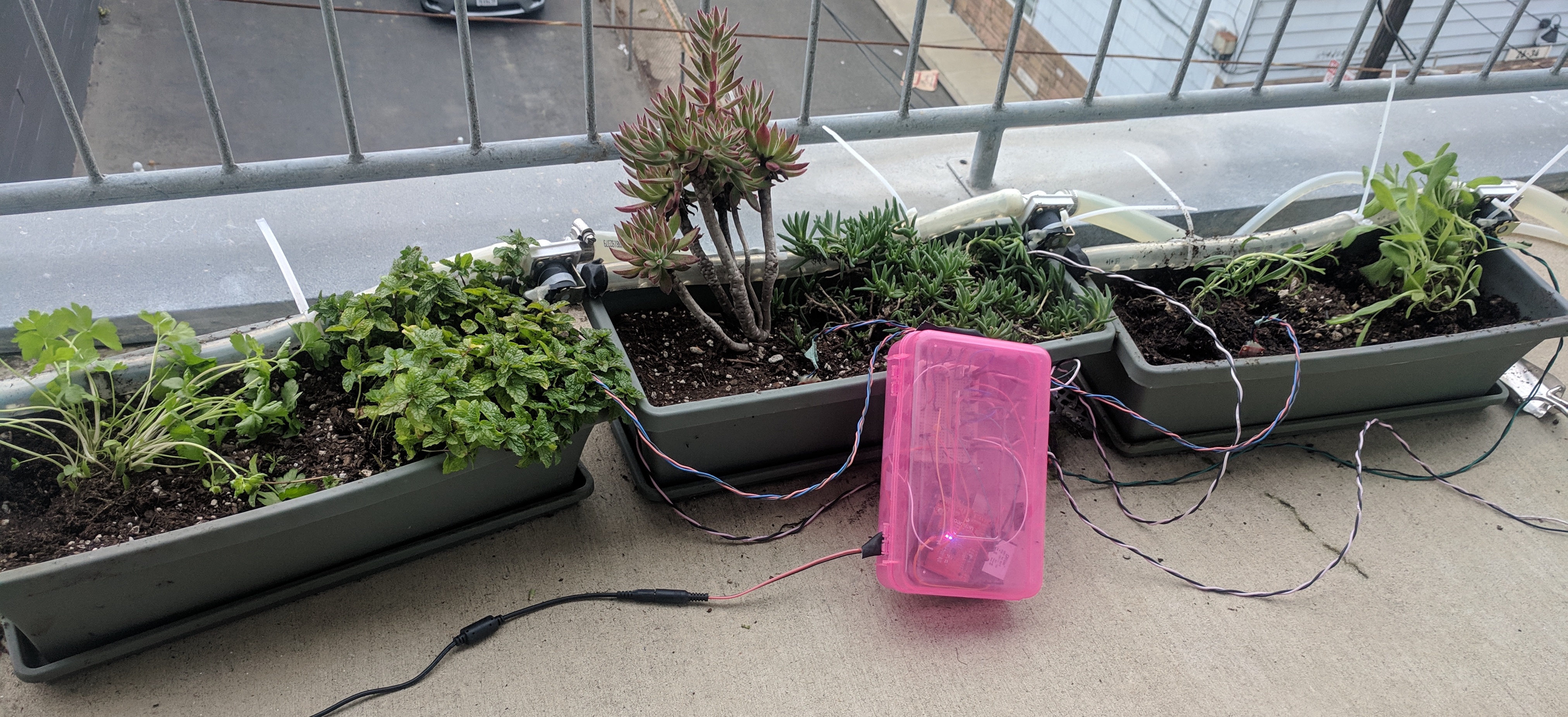

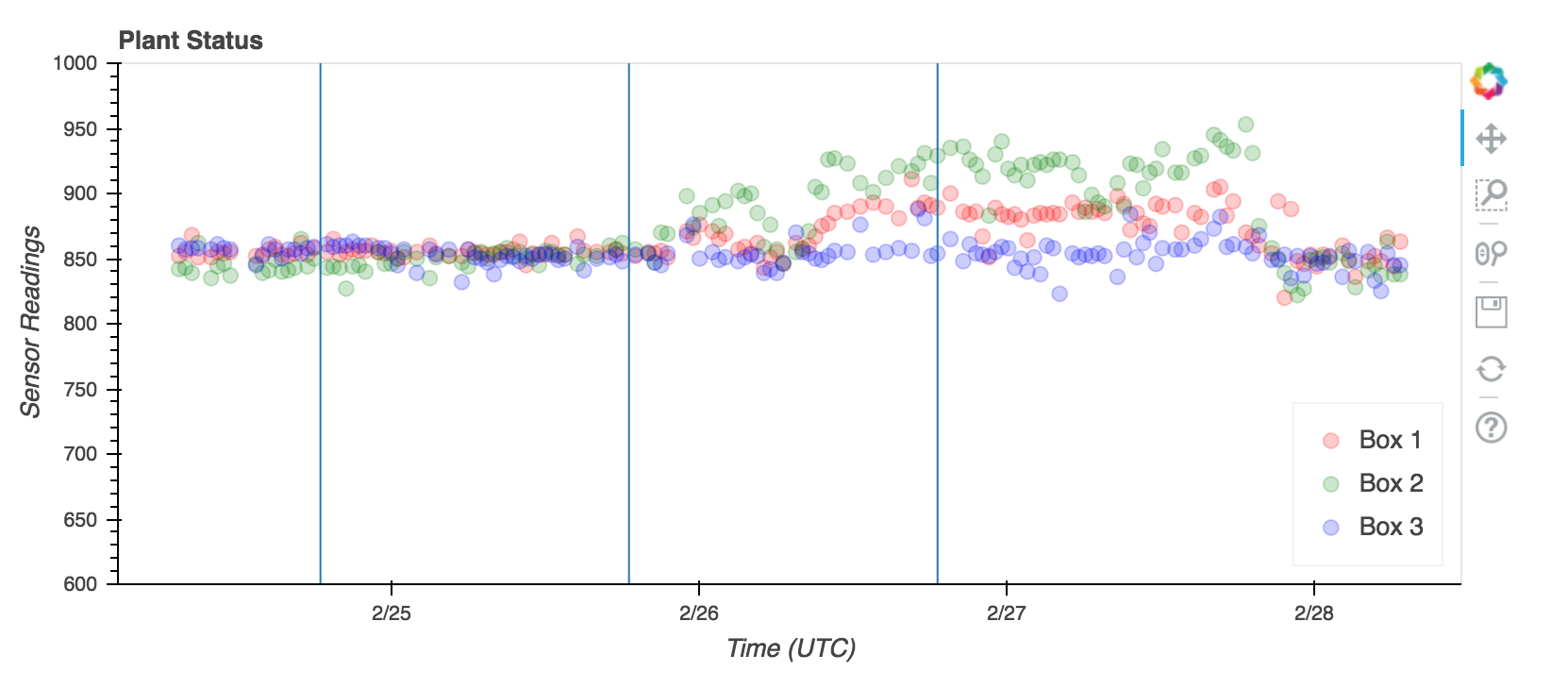
I started working on this project after all my plants died when I went on vacation. It currently waters the plants once per day and monitors the soil moisture. The moisture sensors, as it turns out, aren’t sensitive enough to determine the watering schedule but they make for a nice graph.
The full list of materials is:
- Arduino Uno
- WiFi Shield - ESP8266
- 3 Soil Moisture Sensors
- 3 12V Solenoid Valves
- 3 TIP120 Darlington Transistors
- 3 Kickback Diodes
- DROK LM2596 Switching Regulator
- 12V 35 PSI Water Pump
- 3/8” ID Tubing
- 3/4” ID Tubing
- 3/8” T hose connectors
- 3/8” - 3/4” hose adapters
- Bunch o’ hose clamps
- Teflon tape
- Plants
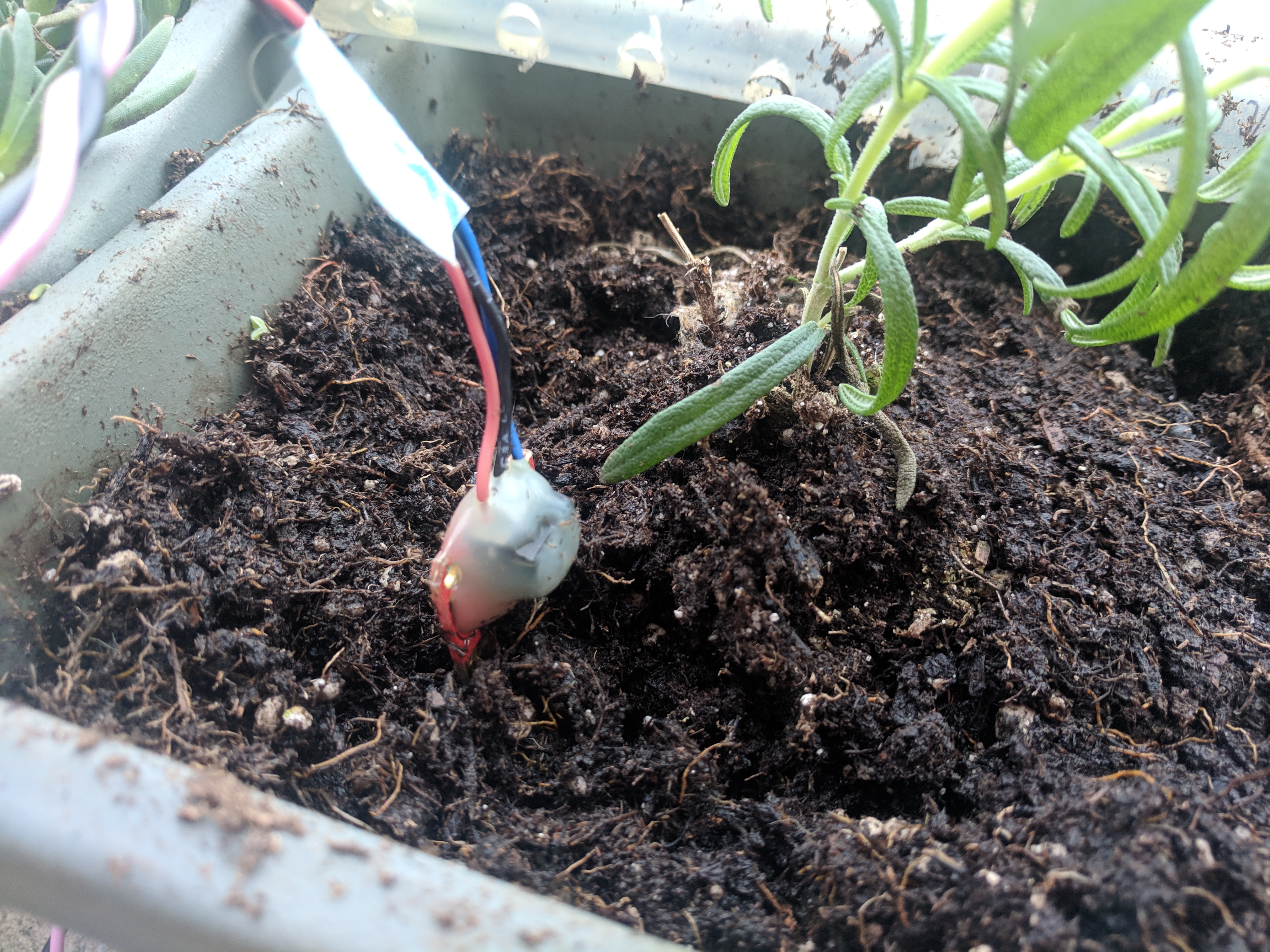
The easiest portion of this is the moisture sensors. Each sensor has three terminals: power, ground and signal. The sensor lasts longer if it’s not powered all the time, so we power it from an output pin. Every half-hour, we set the power pin to high, read a value from each sensor and make a request to a Flask app.

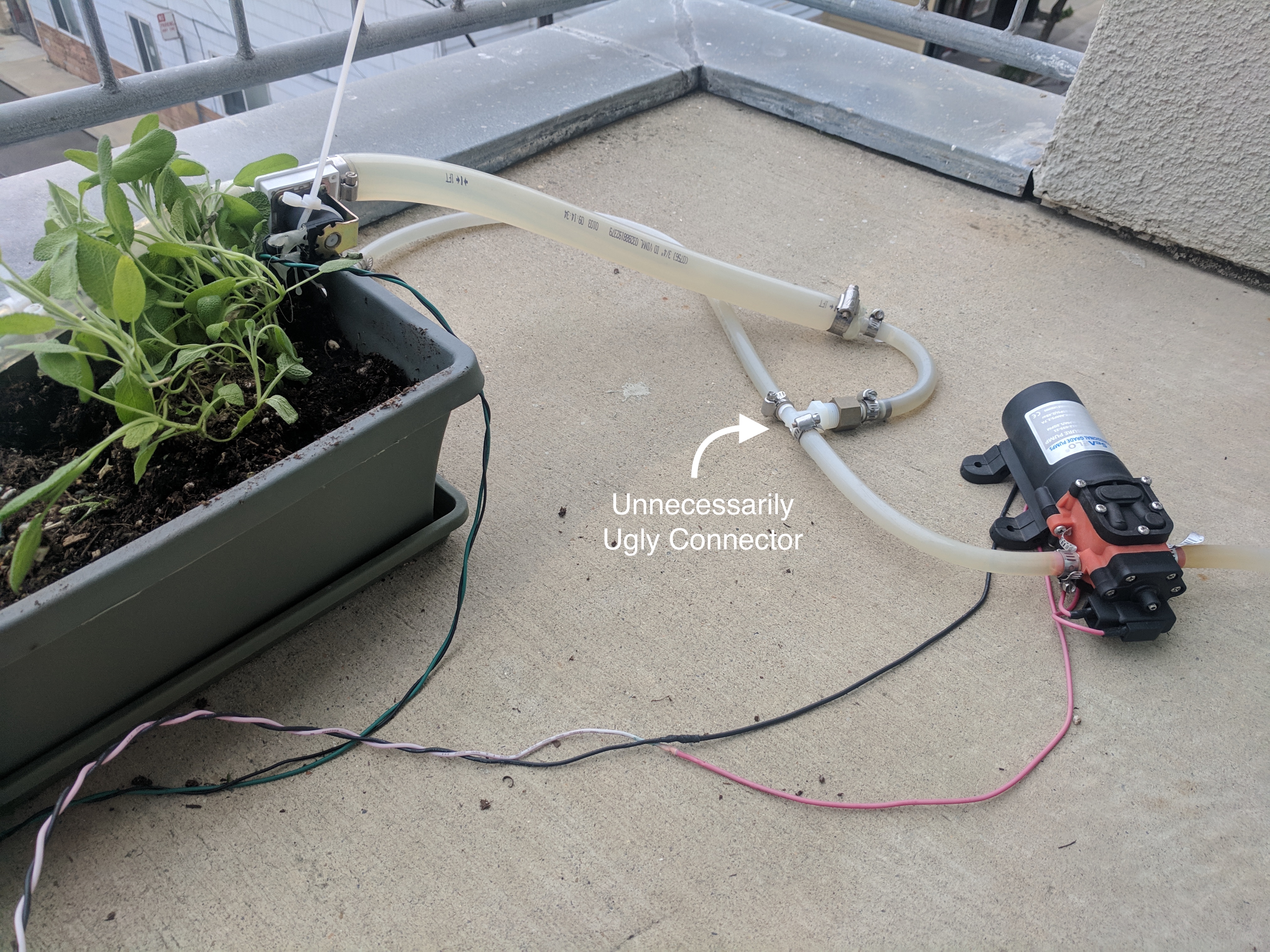
The actual watering was harder. The valves only work properly when pressurized and both the valves and the pump require 12V. Using a switching regulator, we can have a 12V rail for the pump and valves and a 5V rail for the Arduino. The pump can be connected directly to the 12V rail; it will itself turn off when the system in pressurized. The valves are controlled with TIP120 transistors.
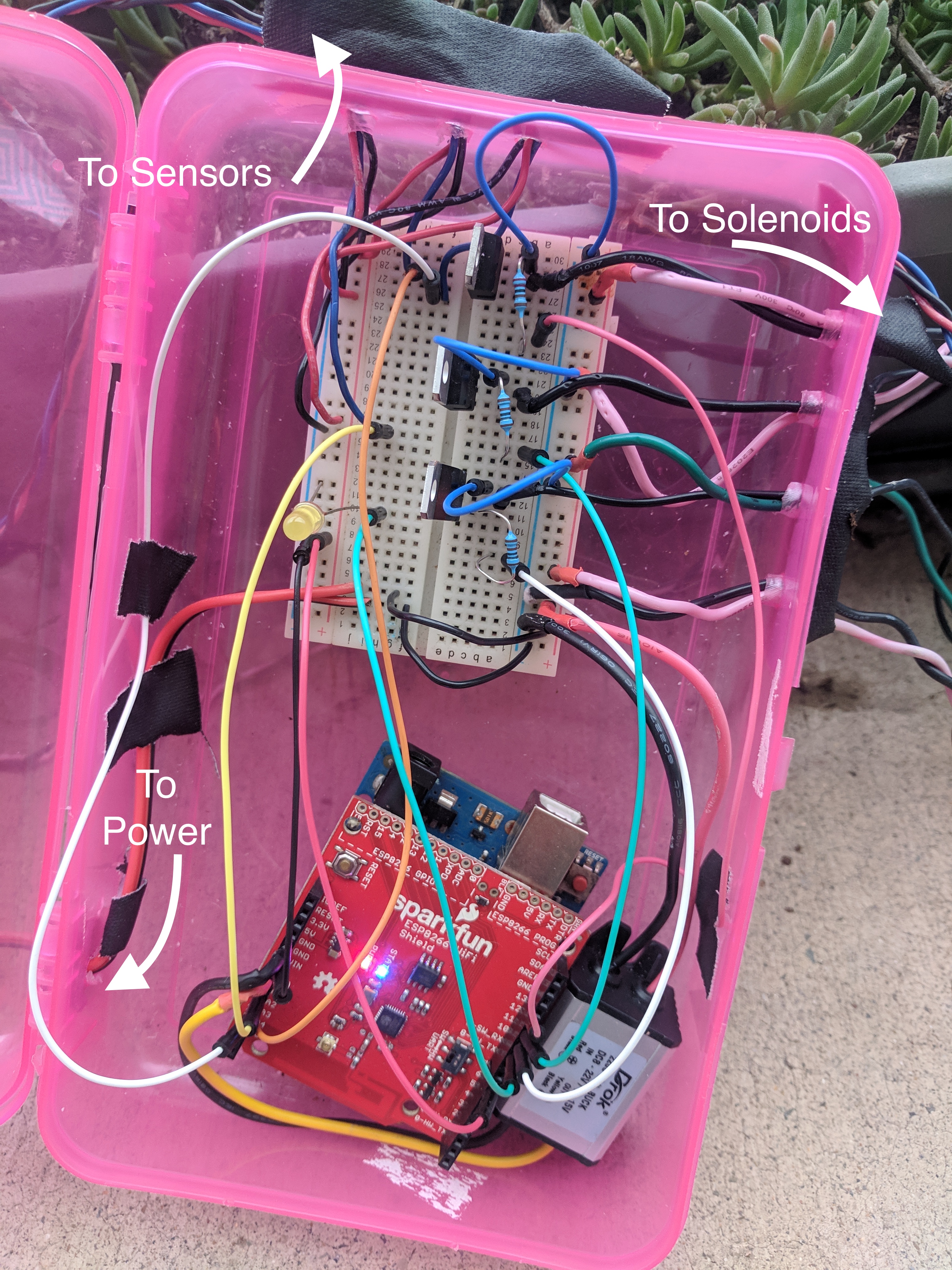
The tubing required a lot of trial and error. The pump output is significantly smaller than the valve inputs and needs to be stepped up with a 3/8”-3/4” adapter. The hardware store didn’t have all the fittings I needed, and I had to combine connectors in a few places. All the connections need to be wrapped in teflon tape and clamped down tightly to maintain pressure. I spent a couple hours turning the system on, finding a leak, tightening the clamp, finding a new leak, etc. Also of note: when the pump is first turned on, all the valves need to opened until there is no air left in the tubes; any air pocket in the tubes will be compressed and eventually pop as the system pressurizes.

Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <SparkFunESP8266WiFi.h>
//////////////////////////////
// WiFi Network Definitions //
//////////////////////////////
const char mySSID[] = "<wifi>";
const char myPSK[] = "<wifi password>";
//////////////////
// HTTP Strings //
//////////////////
const char destServer[] = "<host>";
const String connectionClose = " HTTP/1.1\n"
"Host: <host>\n"
"Connection: close\n\n";
////////////////////
// Pin Variables //
///////////////////
const int sensorPower = 7;
const int sensor1 = A0;
const int sensor2 = A1;
const int sensor3 = A2;
const int solenoid1 = 13;
const int solenoid2 = 12;
const int solenoid3 = 11;
const int signalLight = 10;
////////////////////
// Misc Variables //
///////////////////
int val1 = 0;
int val2 = 0;
int val3 = 0;
unsigned long last_watered;
unsigned long current_time;
const unsigned long day_in_milliseconds = 86400000;
const int sensor_samples = 5;
void setup()
{
pinMode(signalLight, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(signalLight, LOW);
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(sensorPower, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(sensorPower, LOW);
pinMode(solenoid1, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(solenoid1, LOW);
pinMode(solenoid2, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(solenoid2, LOW);
pinMode(solenoid3, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(solenoid3, LOW);
// verifies communication with the WiFi shield, and sets it up.
initializeESP8266();
connectESP8266(); // connects to the defined WiFi network.
// displayConnectInfo prints the Shield's local IP
// and the network it's connected to.
displayConnectInfo();
last_watered = millis();
waterAll();
}
int averageVal(int sensor) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i < sensor_samples; i++){
sum += analogRead(sensor);
delay(100);
}
return sum/sensor_samples;
}
void waterPlant(int solenoidPin) {
Serial.println(F("Watering a plant"));
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, HIGH); //Switch Solenoid ON
delay(5000); //Wait
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, LOW); //Switch Solenoid OFF
}
void waterAll() {
waterPlant(solenoid1);
delay(5000);
waterPlant(solenoid2);
delay(5000);
waterPlant(solenoid3);
waterUpdate();
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(sensorPower, HIGH);
delay(10);//wait 10 milliseconds
val1 = averageVal(sensor1);
val2 = averageVal(sensor2);
val3 = averageVal(sensor3);
digitalWrite(sensorPower, LOW);
digitalWrite(signalLight, HIGH);
sensorUpdate(val1, val2, val3);
Serial.println(F("Request complete"));
delay(10);
digitalWrite(signalLight, LOW);
if (millis() < last_watered || ( millis() - last_watered ) > day_in_milliseconds) {
last_watered = millis();
waterAll();
}
delay(1800000);
}
void initializeESP8266()
{
int test = esp8266.begin();
if (test != true)
{
Serial.println(F("Error talking to ESP8266."));
errorLoop(test);
}
Serial.println(F("ESP8266 Shield Present"));
}
// connect Wifi Shield
void connectESP8266()
{
int retVal = esp8266.getMode();
if (retVal != ESP8266_MODE_STA)
{
retVal = esp8266.setMode(ESP8266_MODE_STA);
if (retVal < 0)
{
Serial.println(F("Error setting mode."));
errorLoop(retVal);
}
}
Serial.println(F("Mode set to station"));
retVal = esp8266.status();
Serial.print(F("status is "));
Serial.println(retVal);
if (retVal <= 0)
{
Serial.print(F("Connecting to "));
Serial.println(mySSID);
retVal = esp8266.connect(mySSID, myPSK);
if (retVal < 0)
{
Serial.println(F("Error connecting"));
errorLoop(retVal);
}
}
}
void displayConnectInfo()
{
char connectedSSID[24];
memset(connectedSSID, 0, 24);
int retVal = esp8266.getAP(connectedSSID);
IPAddress myIP = esp8266.localIP();
Serial.print(F("My IP: ")); Serial.println(myIP);
}
// Record moisture sensor values
void sensorUpdate(int box1, int box2, int box3) {
String request;
request += "GET /moisture?";
request += "box1=";
request += box1;
request += "&box2=";
request += box2;
request += "&box3=";
request += box3;
request += connectionClose;
makeRequest(request);
}
// Record plants watered
void waterUpdate() {
String request;
request = "GET /watered" + connectionClose;
makeRequest(request);
}
// write request to ESP8266 client
void makeRequest(String request)
{
ESP8266Client client;
int retVal = client.connect(destServer, 80);
Serial.print(F("connection is "));
Serial.println(retVal);
if (retVal <= 0)
{
Serial.println(F("Failed to connect to server."));
return;
}
char buff[12];
Serial.write(request.c_str());
client.print(request);
while (client.available())
client.read(); // read() gets the FIFO char
if (client.connected())
client.stop(); // stop() closes a TCP connection.
}
// errorLoop prints an error code, then loops forever.
void errorLoop(int error)
{
Serial.print(F("Error: ")); Serial.println(error);
Serial.println(F("Looping forever."));
for (;;)
;
}